Call Us For Physics Coaching : +91 - 8804659499
 Join FREE Demo Classes - Now!!!
Join FREE Demo Classes - Now!!!
The Big Bang Theory is the prevailing cosmological model explaining the origin and evolution of the universe. Here is an overview of the Big Bang Theory, its key concepts, evidence, and implications:
Overview
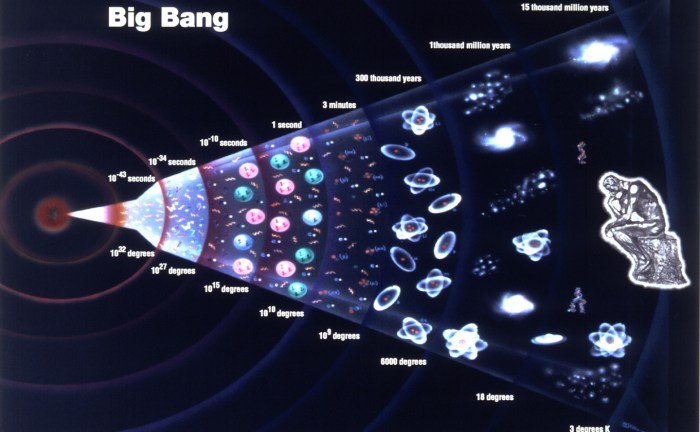
The Big Bang Theory posits that the universe began approximately 13.8 billion years ago from an extremely hot, dense state and has been expanding ever since. This theory provides a comprehensive explanation for a wide range of observed phenomena, including the cosmic microwave background radiation, the large-scale structure of the universe, and the abundance of light elements.
Key Concepts
-
Singularity
- The theory suggests that the universe originated from a singularity, a point of infinite density and temperature where the known laws of physics cease to operate.
-
Expansion
- From this singular state, the universe began to expand, leading to a decrease in density and temperature over time.
-
Inflation
- A rapid exponential expansion of the universe occurred within the first fraction of a second after the Big Bang, solving several cosmological puzzles, such as the horizon and flatness problems.
-
Nucleosynthesis
- As the universe cooled, protons and neutrons combined to form the nuclei of the lightest elements, such as hydrogen, helium, and traces of lithium, within the first few minutes.
-
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB)
- About 380,000 years after the Big Bang, the universe cooled enough for electrons and protons to combine into neutral hydrogen atoms, making the universe transparent to radiation. This event released the CMB, a faint glow detectable in all directions.
-
Formation of Structure
- Over billions of years, small initial density fluctuations grew under the influence of gravity, leading to the formation of stars, galaxies, and larger structures.
Evidence Supporting the Big Bang Theory
-
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation
- Discovered in 1965 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, the CMB is the afterglow of the Big Bang and provides a snapshot of the early universe. It has been mapped in great detail by missions such as COBE, WMAP, and Planck.
-
Hubble's Law
- Edwin Hubble's observation that galaxies are moving away from us with a velocity proportional to their distance supports the idea of an expanding universe. This relationship is expressed as v=H0dv, where v is the galaxy's recessional velocity, H0 is the Hubble constant, and ddd is the distance to the galaxy.
-
Abundance of Light Elements
- The observed abundances of hydrogen, helium, and lithium in the universe match the predictions of Big Bang nucleosynthesis models.
-
Large-Scale Structure
- The distribution of galaxies and cosmic voids in the universe can be explained by the growth of initial density fluctuations under the influence of gravity.
-
Galactic Evolution and Distribution
- Observations of distant galaxies and quasars show that the universe was different in the past, supporting the idea of a dynamic, evolving universe.
Implications
-
Age of the Universe
- The Big Bang Theory provides an estimate for the age of the universe, about 13.8 billion years, derived from measurements of the CMB and the expansion rate.
-
Cosmological Principle
- The theory assumes that the universe is homogeneous and isotropic on large scales, meaning it looks the same in all directions and at any location.
-
Dark Matter and Dark Energy
- Observations suggest that ordinary matter makes up only about 5% of the universe's total energy density, with the rest consisting of dark matter (27%) and dark energy (68%). These components play crucial roles in the universe's structure and expansion.
Challenges and Open Questions
-
Singularity and Quantum Gravity
- The initial singularity poses a challenge as the known laws of physics, including general relativity, break down. A theory of quantum gravity is needed to describe the conditions at the very beginning.
-
Nature of Dark Matter and Dark Energy
- The exact nature of dark matter and dark energy remains unknown, and understanding these components is one of the biggest challenges in modern cosmology.
-
Inflation Mechanism
- While inflation theory solves several problems of the standard Big Bang model, the exact mechanism and the field driving inflation are still subjects of active research.
Conclusion
The Big Bang Theory is a robust and well-supported model that explains the origin and evolution of the universe. It is backed by extensive observational evidence and provides a framework for understanding the large-scale structure and dynamics of the cosmos. However, many questions remain, particularly concerning the very early universe and the fundamental nature of dark matter and dark energy. Ongoing and future observations, along with theoretical advancements, aim to address these mysteries and further refine our understanding of the universe's beginnings.
Tags : The Big Bang Theory,Physics, Big Bangs, Big Bang in Physics and Philosophy of Science, Big Bang Exploring what these Laws are, How Big Bang Operate, and what they Signify about the Universe